Energy resources of the world
The Academy of Technology has been looking into the possibility of using alternative sources for energy to power the future.
Energy resources are divided into four main categories. Non-renewable resources are limited in supply and can’t be recreated. Renewable resources rely on natural systems to produce power, but only at the rate that they’re replaced. Nuclear energy is produced with the use of nuclear processes or plants, which also tend to generate radioactive waste that can harm plants and animals over time. There are also secondary energy resources, or fuel sources. These include several types of energy – thermal, electrical, nuclear, chemical and mechanical. We use these for power generation mostly.
Assessing the world’s energy resources will allow for a more sustainable approach to development.
Wood, the only energy resource worth mentioning until the 19th century, is still used in many areas. Historically, the discovery of the steam engine led to a huge surge in coal production. The invention of the internal combustion engine required a sharp increase in oil production. And as society has shifted, natural gas use has grown. Hydro and nuclear power eventually emerged to take their place in the global economy. However, they never became top energy sources for world economies. The “oil era” gave rise to increasingly intensive economic development, which in turn meant an increase in production and consumption of goods should be indispensable. In the last few decades, the amount of energy consumed has doubled every 13-14 years.
Non-renewable energy resources
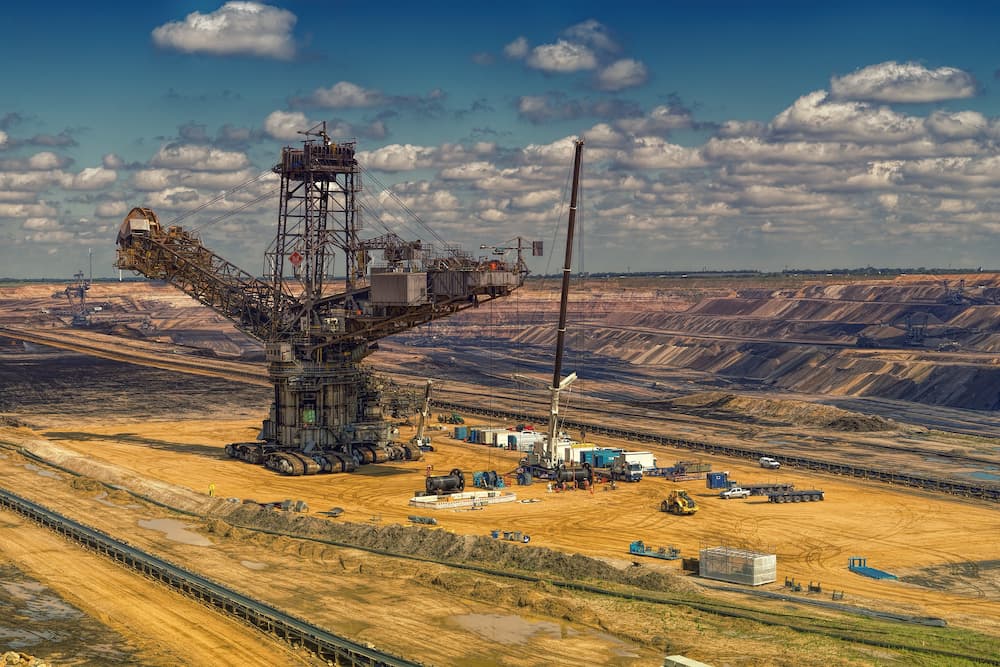
Non-renewable energy sources are all types of fossil fuels, including oil, natural gas, coal (brown coal), and oil shale. Coal plays a big role in the world’s reserves of fossil fuels (up to 60%). Oil and natural gas are the second-most important types of non-renewable energy sources. When estimating reserves, there are three main categories: Proved Reserves, Ending Inferred Reserves, and Probable Reserves. Probable reserves are harder to quantify because it depicts the estimated amount of oil that is likely in place in an area.
In 2010, more than 91% of all energy produced by people on Earth was made from these fossil fuels. There are environmental risks to pumping greenhouse gases into the air, but our reliance on these fuels is not going anywhere. US agency EIA forecasts that by 2040, the share of fossil fuels will decrease to 78% while energy consumption will grow by 56% from 2010 to 2040. These are some of the huge problems in modern civilization, all associated with depletion in non-renewable resources, pollution and global warming.
The basis of power engineering is formed by thermal power plants (TPP), using the chemical energy of fossil fuels. In 2010, fossil fuel TPPs provided more than 67% of the total output of all power plants in the world.
Oil
Proven oil reserves from oil fields that we know of & have thoroughly tested are 1,638-1687 billions barrels. One report says there could be up to 9,800-18,900 billion barrels in total back there that we haven’t yet discovered or found a way to get out of them.
Over the course of 2010, oil accounted for 32% of all energy and 4.6% of electricity.
Along with being used as a source of energy, oil is also used to make the other chemical products. According to IEA in 2010, 16.8% of oil products went for non-energy purposes.
Natural gas
Natural gas is a widely used fuel for a variety of purposes. From heating buildings, to powering cars and even powering generators, it is important to consider what you need from your natural gas supplier.
The proven recoverable reserves of natural gas in 2012 were, according to various estimates, 185-192 trillion cubic meters. That’s a 39% increase in natural gas reserves since 1992.
According to the IEA, gas accounted for 21% of total energy & 22% of electric power in 2010. As for unaccounted gas, about 5.5% was not used for fuel.
Coal
Coal is the most widespread and used fossil gas. The discovery of its industrial value launched the industrial revolution and, to this day, its consumption rate has been increasing. In 2009, the U.S energy information administration estimated the proven US recoverable world coal reserves to be 946 billion tons. This will allow for current levels of consumption until 2130 at a rate of 5% growth per year. British Petroleum estimates that coal reserves for 2013 totalled 891 billion tons, which will last until 2126.
The IEA estimates that coal was the energy source for 27% of all energy and 40% of electricity in 2010.
Renewable energy resources
Renewable resources are a good alternative for a wide variety of reasons. They can save you time and money, and they’re naturally replenished meaning you won’t run out on a human timescale. Renewable organic resources can come from a variety of sources like natural processes.
In 2010, renewable energy sources accounted for about 13% of global energy consumption (2.3% hydropower, 10% biofuels and waste, 1% alternative energy sources), and about 20% of all electricity (16% hydropower, 3.7% biofuels and alternative energy sources), according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This year, the share of clean energy in the world’s energy consumption is at 11%. This figure is expected to increase by 4% by 2040. The share of renewable energy sources in electricity production was about 20% back in 2010. REN21 says our share is 15% hydro and 5% biofuels and renewables.
According to the International Energy Agency, in 2018 renewable energy sources had a 26% share in electricity production, while 10.1% of the total was produced by nuclear power.
Biofuels
Renewable Energy usually comes from plant and animal-based sources, but also includes waste products from organisms: firewood and chopped wood, pellets and briquettes made with organic industrial waste such as vegetable oil or ethanol. Of the 54-60% biofuels in use at present, a huge chunk is traditional ones, such as firewood and plant residue that are used for heating houses and cooking. 38% of the world’s population rely on traditional forms of biofuel. One of the most popular biofuels for power is pellets. In transport, ethanol is used in a lot of cases and makes up 74% of the market share in 2014. Biodiesel also contributes with 23% and hydrogenated vegetable oil rounds off this percentage to 100%.
Hydropower
Water used to be the primary form of energy and was heavily relied on for technology needs. Water wheels were used to convert the movements of water into mechanical energy which was often transferred through rotating shafts. One way this conversion of mechanical energy was done was by the use of hydro turbines that generated electricity.
Hydroelectric plants are often built on rivers to increase the difference in water levels found there. To insure that there is enough water available for consumption, dams and reservoirs are built throughout the year. The use of hydropower has the following features: the initial investment for the construction of hydropower plants usually requires more capital investment than thermal power plants, but the cost of energy production is lower; Hydroelectric power plants can easily and quickly change the generated power of electricity; large and efficient hydropower plants cannot be built anywhere and are often remote from consumers; the construction of hydroelectric power plants has a significant impact on the environment due to the creation of dams and reservoirs.
Globally there is a significant potential of 9.8 trillion kWh from hydropower which is shared by China, Russia, USA, Zaire, Canada and Brazil.
Alternative energy
Alternative energies include both industries with a long history of success – solar and wind power, and less widespread nascent industries – geothermal energy, biofuel power plants, tidal and wave power plants, and thunderstorm energy.
Nuclear energy
Nuclear power utilizes nuclear energy to generate electricity, as well as thermal energy. Generally, to get nuclear power, a chain reaction of atomic fission of plutonium-239 or uranium-235 nuclei is utilized. It’s also anticipated that in the future, thermonuclear energy will take on controlled nuclear fusion; at present, the industry has not left its experimental reactor stage.
Nuclear energy is produced in nuclear power plants, used on nuclear icebreakers, nuclear submarines. There are also programs to create a nuclear rocket engine.
In 2010, nuclear power provided 12.9% of electricity production and 5.7% of all energy consumed by mankind, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). That’s about 5% of all energy according to the US EIA.
About half of the world’s energy production at nuclear power plants comes from the US and France – significant amounts are produced by nuclear power plants in Russia and China. Out of the 449 operating nuclear power reactors in the world, there are 5 shut down for repairs to their cooling.
Forecasts
It’s estimated that global energy demand will increase by 30% by 2035. This is largely because increased prosperity in developing countries. However, this will be less than the projected growth in world GDP due to improving energy efficiency. It is assumed the demand for oil will grow an average of 0.7% per year until 2035, but the growth rate will slow down. With predictions to grow at 1.6% in demand in the next year, natural gas is in high-demand in Australia & & other countries. Coal consumption will also be increasing until 2020 when China switches to cleaner fuels. To put it simply, the share of gas will become larger than that of coal in the global energy production.

Leave a Reply